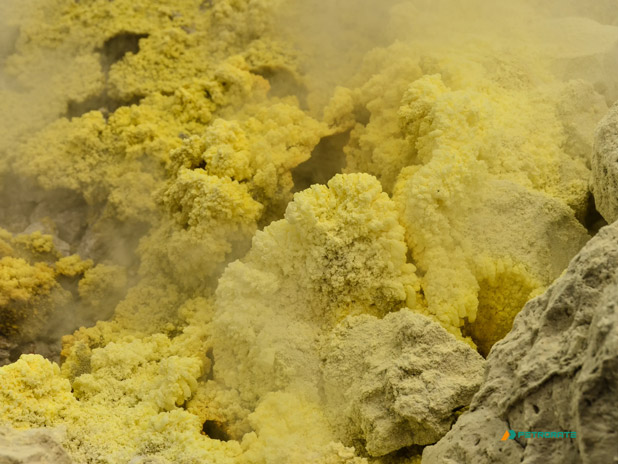
sulphur (S), nonmetallic chemical element belonging to the oxygen group (Group 16 [VIa] of the periodic table), one of the most reactive of the elements. Pure sulfur is a tasteless, odourless, brittle solid that is pale yellow in colour, a poor conductor of electricity, and insoluble in water. It reacts with all metals except gold and platinum, forming sulfides; it also forms compounds with several nonmetallic elements.
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| atomic number | 16 |
| atomic weight | 32.064 |
| melting point | |
| rhombic | 112.8 °C (235 °F) |
| monoclinic | 119 °C (246 °F) |
| boiling point | 444.6 °C (832 °F) |
| density (at 20 °C [68 °F]) | |
| rhombic | 2.07 grams/cm3 |
| monoclinic | 1.96 grams/cm3 |
| oxidation states | −2, +4, +6 |
| electron configuration | 1s22s22p63s23p4 |
Desulfurization equipment in refineries uses advanced technologies such as Sulfur Recovery Units (SRUs) to separate sulfur from acid gases and convert it into usable products.
This process not only reduces air pollution from fossil fuels, but also helps produce pure sulfur.
Various uses of sulphur in various industries and products
- Production of antifreeze and insecticides
- Manufacture of gunpowder and fireworks
- Welding of rubber
- Manufacture of paper and bleaching materials
- Ammonium or sodium thiosulfate (a fixing agent in photography)
- Electrical insulation
- Rayon